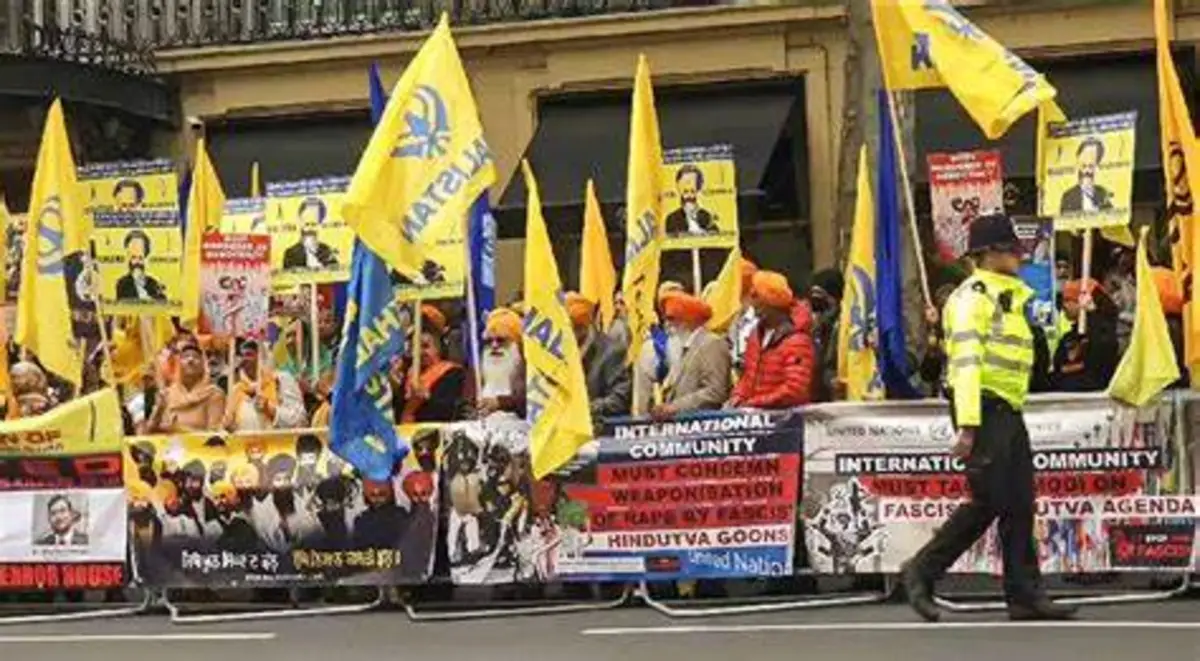
Attack On Indian Embassy
- Law enforcement agencies quickly secure the area to ensure the safety of personnel and prevent further attacks Investigators collect physical evidence of Attack on Indian Embassy, such as CCTV footage, fingerprints, and any left-behind items that could be linked to the perpetrators.
Table of Contents
Investigation: Attack On Indian Embassy
- Witness Interviews: Attack On Indian Embassy Officials conduct interviews with witnesses who were present during the attack to gather firsthand accounts.
- Forensic Analysis: Forensic experts analyze the collected evidence to identify the methods and materials used in the attack.
Tracking and Arrest: Attack on Indian Embassy
- Identifying Suspects: Using the evidence and witness statements, investigators work to identify potential suspects.
- International Cooperation: If the suspects are believed to be in another country, as in the case of the UK resident, international law enforcement cooperation is crucial.
Prosecution: Attack On Indian Embassy
- Charges and Trial: Once sufficient evidence is gathered, charges are filed, and the case is brought to trial.
- Sentencing: If found guilty, the court will sentence the perpetrators according to the severity of their crimes.
Prevention: Attack On Indian Embassy
- Security Review: Attack On Indian Embassy Post-investigation, embassies often review and enhance their security measures to prevent future incidents.
- Intelligence Sharing: Agencies share intelligence to help other embassies and consulates be aware of potential threats.
Security measures at Indian embassies
Security at Indian embassies and consulates around the world is a critical concern, especially in light of any threats or incidents. Here are some general measures that are typically implemented to ensure the safety of diplomatic missions:
Physical Security
- Perimeter Security: This includes barriers, fencing, and gates to prevent unauthorized access.
- Surveillance Systems: CCTV cameras are installed to monitor the embassy’s exterior and interior.
- Access Control: Entry to the embassy is strictly regulated, often involving security checks and visitor screening.
Personnel Security
- Trained Guards: Security personnel are deployed to patrol the premises and respond to incidents.
- Background Checks: Staff and visitors may undergo background checks to identify potential risks.
Procedural Measures
- Emergency Protocols: Embassies have plans in place for evacuation and lockdowns in case of an emergency.
- Information Security: Sensitive information is protected through secure communication channels and data storage.
International Cooperation
- Host Country Support: Local law enforcement agencies often provide additional security and assistance when needed.
- Intelligence Sharing: Embassies may share intelligence with other diplomatic missions to prevent security breaches.
Continuous Assessment
- Security Audits: Regular assessments are conducted to identify vulnerabilities and improve security measures.
- Training: Staff are trained in security awareness and emergency response procedures.
Specific incident where security measures were effective
One notable incident where security measures proved effective was during the Mumbai attacks in November 2008, also known as ‘26/11’. This tragic event revealed vulnerabilities in India’s security apparatus, but it also led to significant reforms and improvements in the country’s counter-terrorism capabilities.

The Mumbai Attacks
- Initial Attack: Multiple locations in Mumbai were targeted by terrorists, leading to widespread chaos.
- Security Response: Despite initial setbacks, Indian security forces, including the National Security Guard (NSG), mobilized to counter the attackers.
Post-Attack Reforms
- Enhanced Training: Security personnel received improved training to handle such incidents.
- Upgraded Equipment: The acquisition of modern equipment and weapons to better equip the first responders.
- Intelligence Coordination: Improved intelligence-sharing mechanisms between different agencies.
Effective Outcomes
- Prevention of Further Attacks: The reforms and new measures have helped in preventing similar large-scale attacks.
- Quick Response: The response time to any potential threat has been significantly reduced.
The effectiveness of these security measures was not only in the immediate handling of the attack but also in the long-term improvements made to prevent future incidents.
The Mumbai attacks in November 2008 had a profound impact on India’s security policies, leading to several significant changes:
Institutional Reforms
- Creation of the NIA: The National Investigation Agency (NIA) was established to combat terror in India.
- Strengthening of Intelligence: There was an increased focus on improving intelligence gathering and sharing.
Policy Changes
- Counterterrorism Laws: India reviewed and revised its counterterrorism laws to be more effective.
- Coastal Security: The attacks exposed vulnerabilities in coastal security, leading to its strengthening.
Security Upgrades
- Modern Equipment: Security forces were equipped with modern weapons and communication systems.
- Training: There was a push for better training of police and security personnel.
International Collaboration
- Global Partnerships: India sought to enhance international partnerships to combat terrorism.
- Focus on Terrorism: The attacks prompted India to prioritize the issue of terrorism on the world stage.


Pingback: Earthquake Shakes Java Island in Indonesia 2024: Destruction